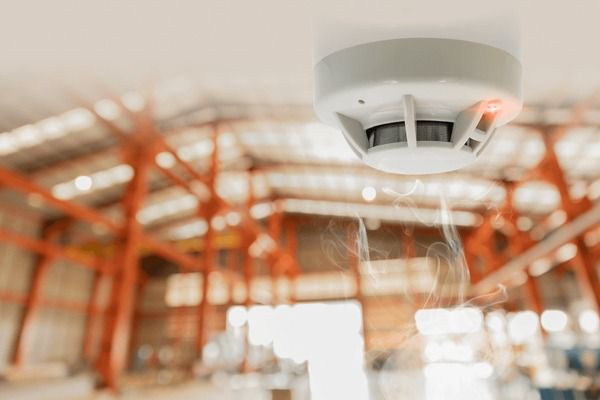

Fire detection and alarm systems are essential components of building safety, designed to identify the presence of fire and alert occupants to evacuate swiftly. These systems play a critical role in protecting lives and property by providing early warnings before a fire can spread uncontrollably. In this article, we’ll explore how fire detection and alarm systems work, the different types of systems available, and how they contribute to overall fire safety.
The Importance of Fire Detection and Alarm Systems
Fires can spread rapidly, especially in enclosed spaces like homes, offices, and industrial buildings. The longer it takes to detect a fire, the greater the risk to lives and property. Fire detection and alarm systems act as an early warning mechanism, detecting the presence of smoke, heat, or fire in its initial stages. This early detection allows occupants to evacuate the building before the fire intensifies and gives emergency responders more time to arrive and control the situation.
In some cases, particularly in large buildings or facilities with complex layouts, it can be challenging for individuals to notice a fire in time. Fire alarms provide clear auditory and visual signals that immediately alert everyone, ensuring that people are made aware of the danger even if they are far from the fire’s origin.
How Fire Detection and Alarm Systems Work
Fire detection and alarm systems are composed of several key components that work together to identify a fire and trigger alarms. These components include:
- Detectors: The heart of any fire detection system, detectors are designed to sense the early signs of fire. There are three main types of detectors used in fire alarms:
- Smoke Detectors: These are the most common and detect particles in the air that result from combustion. Smoke detectors can be ionization-based (for fast-burning fires) or photoelectric (better for detecting slow, smoldering fires).
- Heat Detectors: These detect increases in temperature. Heat detectors are often used in areas where smoke detectors might give false alarms, such as kitchens or industrial spaces.
- Flame Detectors: These are specialized detectors that identify the presence of flames or infrared light. They are typically used in high-risk environments such as chemical plants or refineries.
- Alarm Devices: Once the detectors sense fire or smoke, the system triggers alarms throughout the building. These alarms consist of:
- Audible Alarms: Loud sirens or bells that alert occupants of the fire.
- Visual Alarms: Flashing lights, often red or white, that provide visual warnings for people who may not be able to hear the alarms, such as those with hearing impairments.
- Control Panel: The control panel is the central hub of the fire detection and alarm system. It receives signals from detectors, processes the data, and activates alarms when a fire is detected. The control panel may also notify emergency services directly or provide information to building managers about the fire’s location.
- Manual Call Points: These are devices, often mounted on walls, that allow occupants to manually activate the fire alarm system in case they see a fire. When the glass of a manual call point is broken, the alarm is triggered immediately.
Types of Fire Detection and Alarm Systems
Fire detection and alarm systems come in several different types, each suited to specific environments and fire safety needs.
- Conventional Fire Alarm Systems
Conventional systems divide a building into different zones. Each zone has detectors wired to the control panel. When an alarm is triggered, the control panel identifies which zone the fire is in, but it does not provide specific information about which detector or area within the zone was activated. Conventional systems are more cost-effective and are ideal for smaller buildings like offices or schools. - Addressable Fire Alarm Systems
Addressable systems are more advanced, providing detailed information about the specific detector that was triggered. Each detector has its own unique address, allowing building managers or emergency services to pinpoint the exact location of the fire. These systems are suitable for larger or more complex buildings, such as high-rise apartments, hospitals, or industrial facilities. - Wireless Fire Alarm Systems
Wireless fire alarm systems use radio signals to communicate between detectors and the control panel. These systems are particularly useful in buildings where wiring would be difficult or invasive, such as historical buildings or structures with complex layouts. - Interlinked Smoke Alarms
These alarms are commonly used in homes. When one smoke detector is triggered, all the alarms in the home will sound simultaneously, providing widespread warnings. This ensures that everyone in the home, regardless of where they are, is aware of the fire.
Benefits of Fire Detection and Alarm Systems
Fire detection and alarm systems offer a range of benefits that make them an indispensable part of building safety.
- Early Warning
The most significant advantage of fire detection and alarm systems is their ability to provide early warning of a fire. Early detection can save lives by giving occupants more time to escape, especially in large or multi-story buildings where it can take longer to reach exits.
- Protection of Property
Early fire detection can also minimize damage to property. If a fire is detected and responded to quickly, the spread of flames and smoke can be limited, reducing the overall impact on the building and its contents. Many systems can also be connected to fire suppression systems, such as sprinklers, which can automatically activate to extinguish or control the fire. - Compliance with Safety Regulations
Many countries, including Indonesia, have fire safety regulations that require the installation of fire detection and alarm systems in certain types of buildings. Complying with these regulations helps ensure that buildings are safe for occupants and that building owners are not exposed to legal liabilities. - Insurance Benefits
Installing fire detection and alarm systems can lead to lower insurance premiums, as insurers view these systems as reducing the risk of extensive fire damage. This cost-saving benefit is an added incentive for building owners to invest in high-quality fire alarm systems. - Integration with Other Safety Systems
Modern fire detection systems can be integrated with other safety systems in a building, such as emergency lighting, evacuation systems, and even voice alarm systems. This integration allows for a coordinated and efficient response during an emergency, improving safety outcomes.
Conclusion
Fire detection and alarm systems are a critical component of any building’s safety infrastructure. By providing early warnings, these systems help save lives, protect property, and ensure that buildings comply with fire safety regulations. Whether in homes, offices, or industrial facilities, fire detection and alarm systems are an essential investment in safeguarding people and assets from the devastating effects of fire.




Leave A Comment